If you lost important files on your Mac, recover them in style using the Terminal app. Terminal is a powerful command line tool for macOS that can quickly execute tasks on your machine (or remote ones). There are multiple ways you can use it to restore data.
But if you don’t use Mac Terminal often, it can be confusing to figure out the right commands. This article provides step-by-step instructions for every method to restore deleted files and recover deleted folders with Mac Terminal. Read on.
Set Up Your Terminal App for Recovery
Before attempting any of the methods below, you first have to grant Full Disk Access to the Terminal app. This allows Terminal to modify user-protected data. If you skip this step, some commands won’t work. Here’s how to do it:
- Launch System Settings > Privacy & Secruity. Then, select Full Disk Access in the right menu.
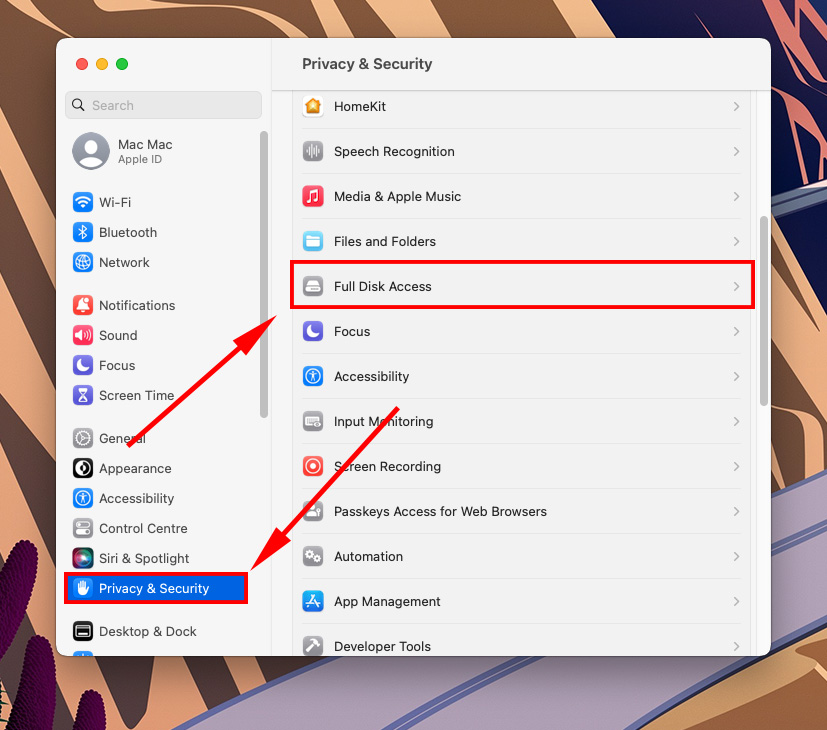
- Locate Terminal in list on the right and tick the box beside it.
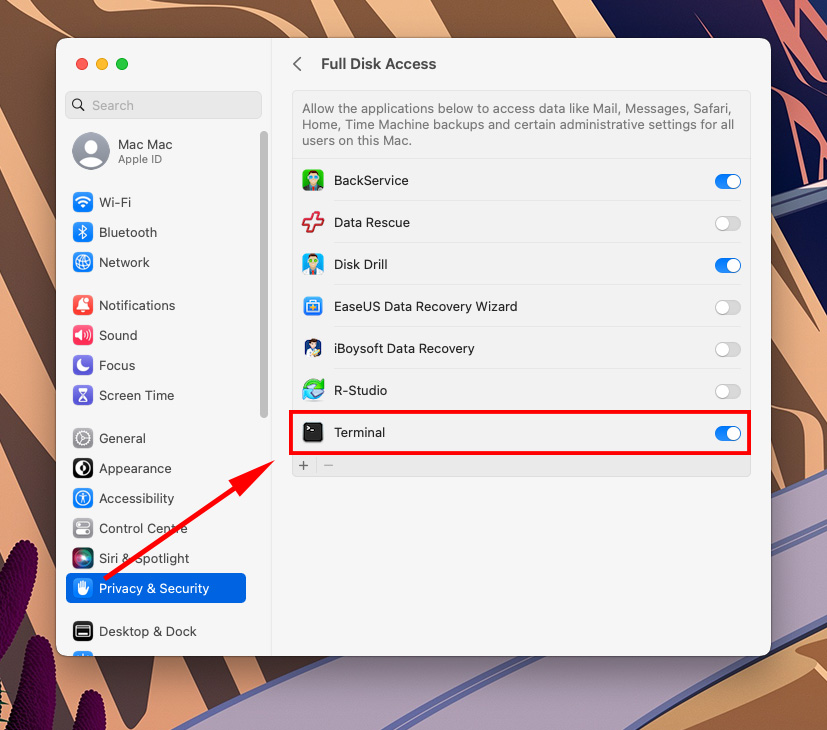
- That’s it! You’ve nov given Full Disk Access to your Terminal.
How to Use Terminal to Recover Deleted Files on Mac
As we talked about earlier, there are different ways to restore data using the Mac Terminal. The method you use depends on what caused the data loss and how you have your Mac set up. Don’t worry – each section clearly describes the situation that the featured method is best suited for.
Option #1: Try to Undelete Files From Trash Using Mac Terminal
If you accidentally deleted your data but you haven’t emptied your Trash folder, you can undelete files or recover deleted folders with the Mac Terminal.
- Open Finder > Applications > Utilities and launch Terminal.

- Type cd .Trash and hit Return.
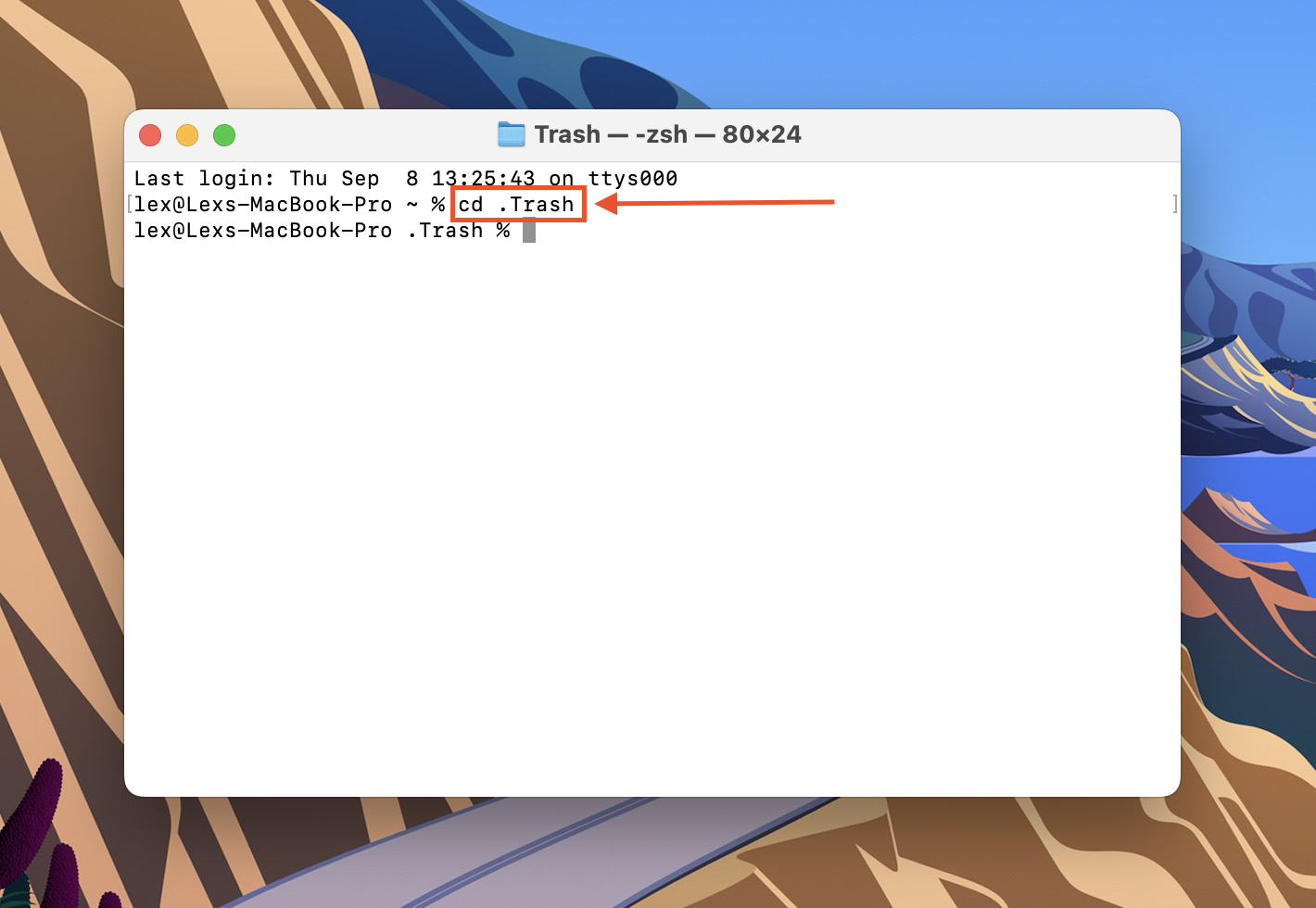
- Type ls -al ~/.Trash and hit Return.
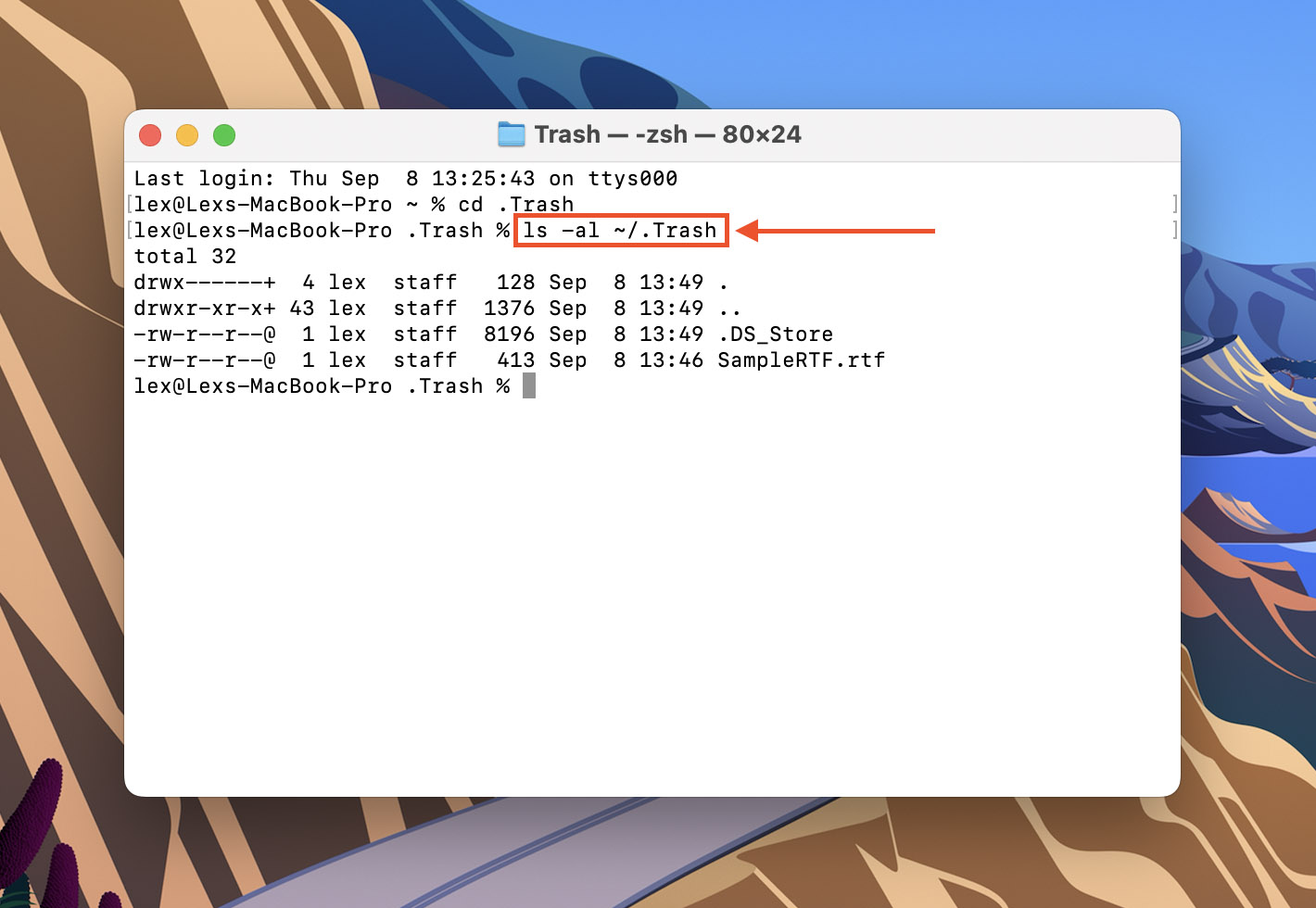
- Type mv yourfile ../ and hit Return. Make sure to replace yourfile with the full name of the file you want to restore.
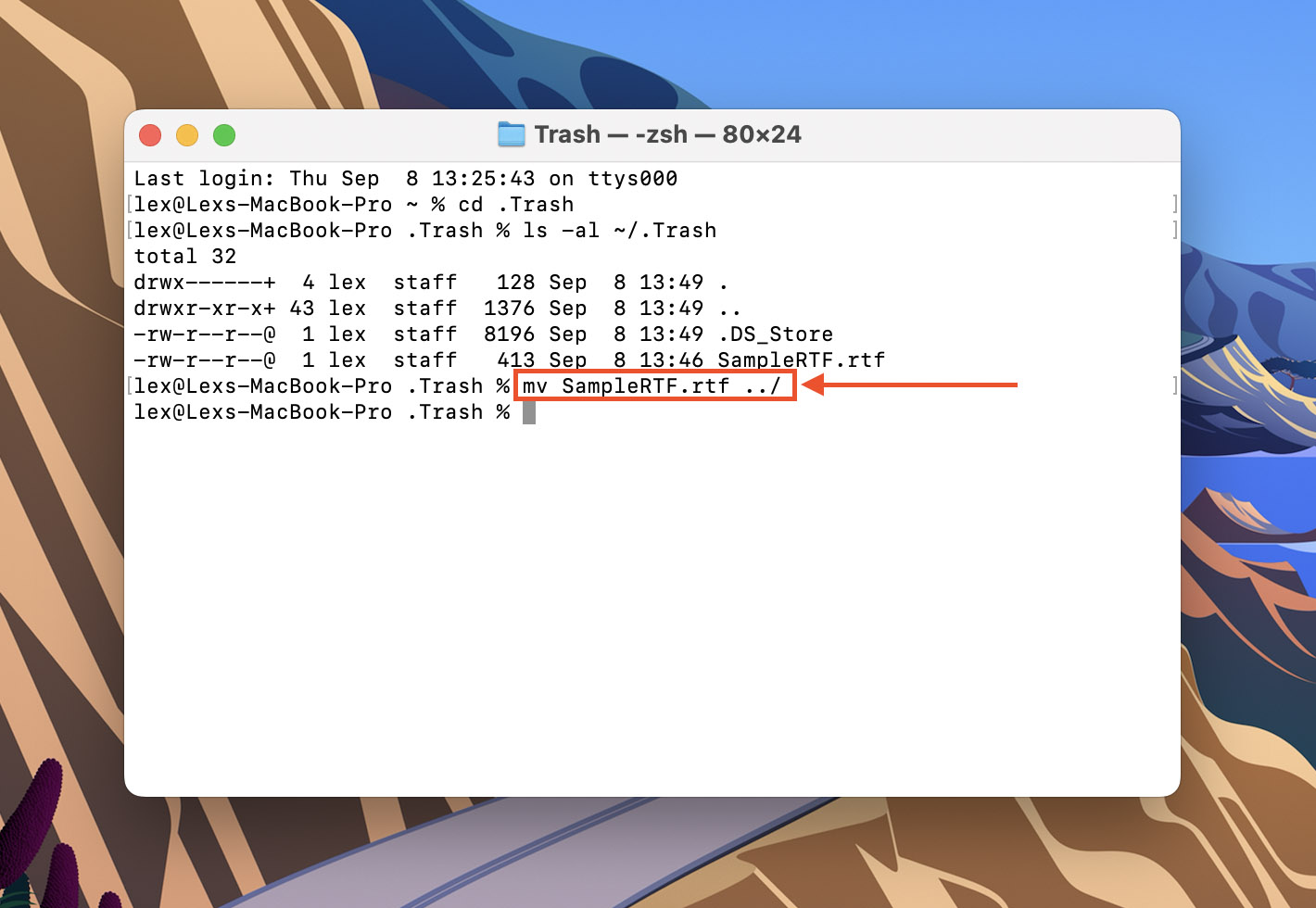
- Type quit and hit Return to close the Terminal app. Your file should be restored to its original folder.
Option #2: Use Mac Terminal to Recover Files from Time Machine Backup
Time Machine is a powerful native Mac tool that lets users save incremental backups of their data. While it offers a great GUI (graphical user interface), you can also use Terminal to restore your backups.
However, note that this method requires Time Machine to have been set up before the data loss occured. If don’t have Time Machine activated, try the other methods in this article.
Info: This method also requires Full Disk Access for the Terminal app. You can enable Full Disk Access in the System Preferences > Security and Privacy tab.
- Launch the Terminal app (Applications > Utilities).
- Type tmutil listbackups and hit return. Take note of the name of the backup you want to restore.
- Type tmutil restore ‘/Volumes/Time Machine Backups/Backups.backupdb/yourcomputername/yourbackupfilename/Macintosh HD/Users/yourusername/Documents/yourfile’ ‘~/Documents/yourfile’ and hit return. But first, replace the following elements:
Change yourcomputername to the name of your Mac. Change yourbackupfilename to whichever you chose in step 2. Change yourusername to your own username. Change Documents (in both instances) to the location that originally stored the file you want to recover. Change yourfile to name of the file you want to restore.
Option #3: Get a Terminal-Based Data Recovery App for Mac
If you emptied your Trash folder and you don’t have a Time Machine backup available, you’ll need to use data recovery software… And yes, we’ll still be using Mac Terminal.
TestDisk/PhotoRec are a 2-in-1 data recovery software that can be controlled entirely through Terminal. And great news: TestDisk/PhotoRec are 100% free open-source software (which can explain the lack of an interface).
- Download and install TestDisk/PhotoRec.
- Launch Terminal (Finder > Applications > Utilities).
- Type sudo photorec and hit return on your keyboard. Enter your password if prompted.
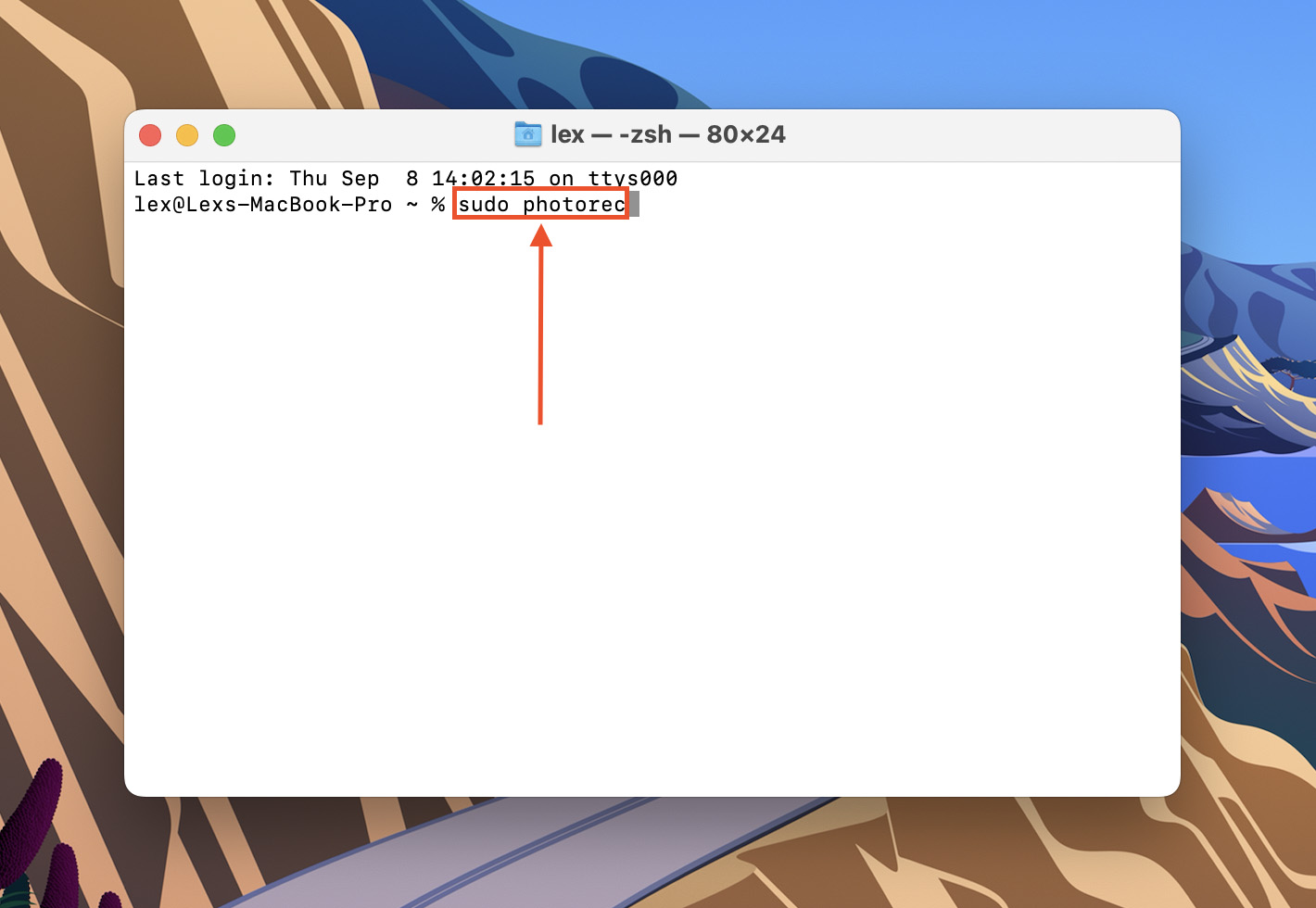
- Use your up and down arrow keys to highlight the drive you want to restore data from. Then, use your left and right arrow keys to highlight Proceed and hit return.
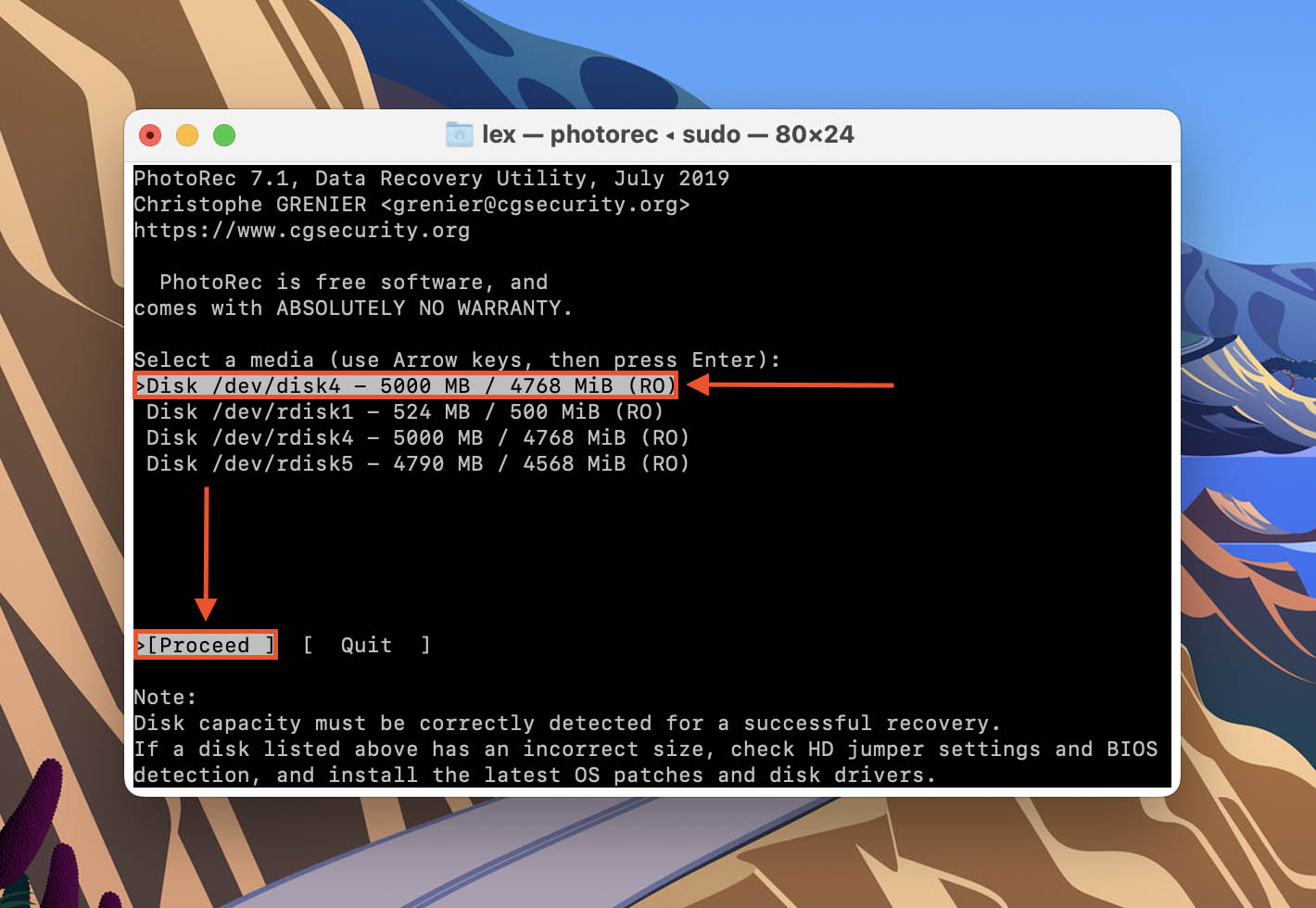
- Use your arrow keys to highlight the partition you want to restore data from. Or you can highlight the Unknown/[Whole disk] entry to scan all patitions. Then, highlight the Search button and hit return. You can also launch the File Opt menu to specify the file types you want to recover.
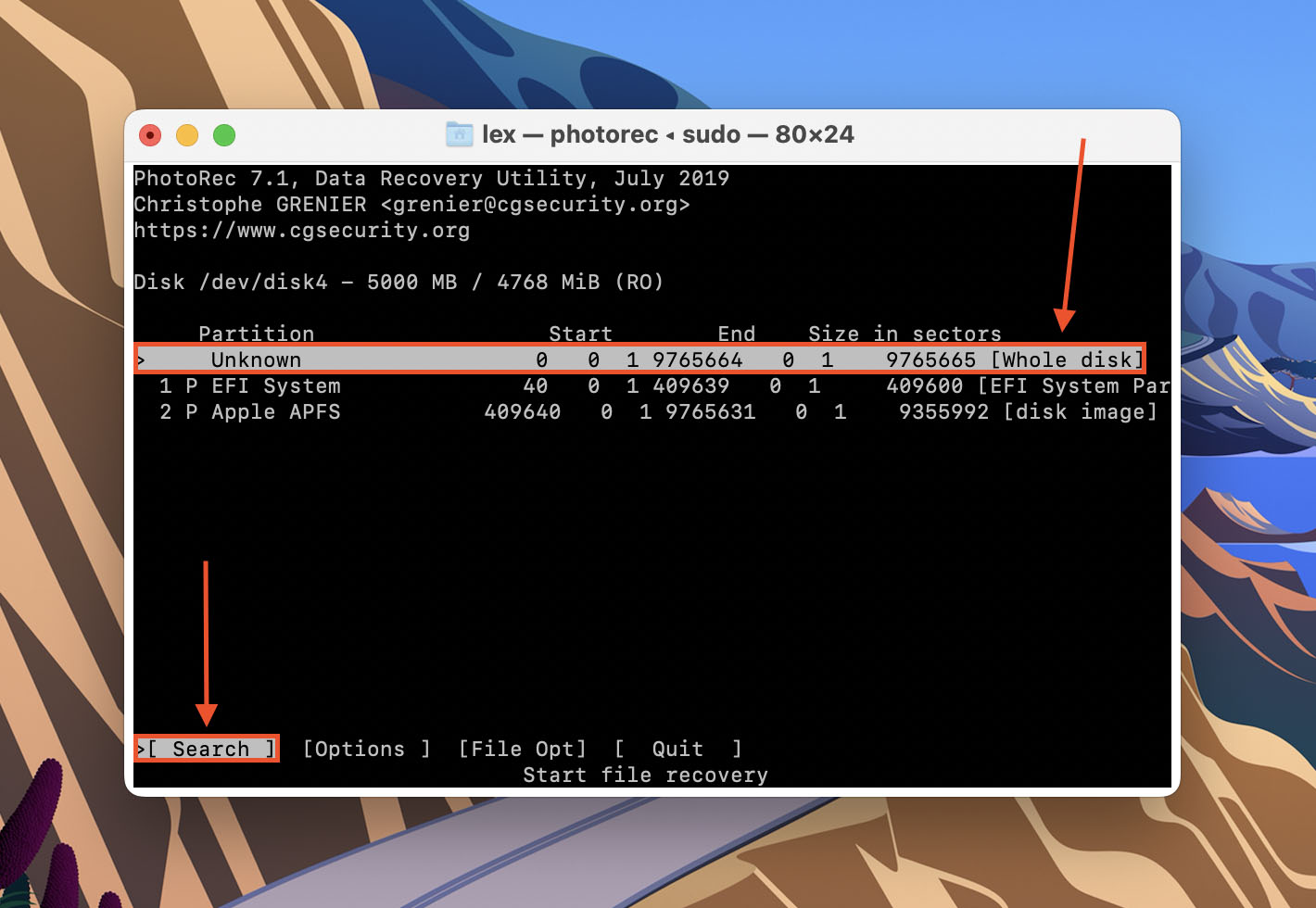
- Highlight Other and hit return.
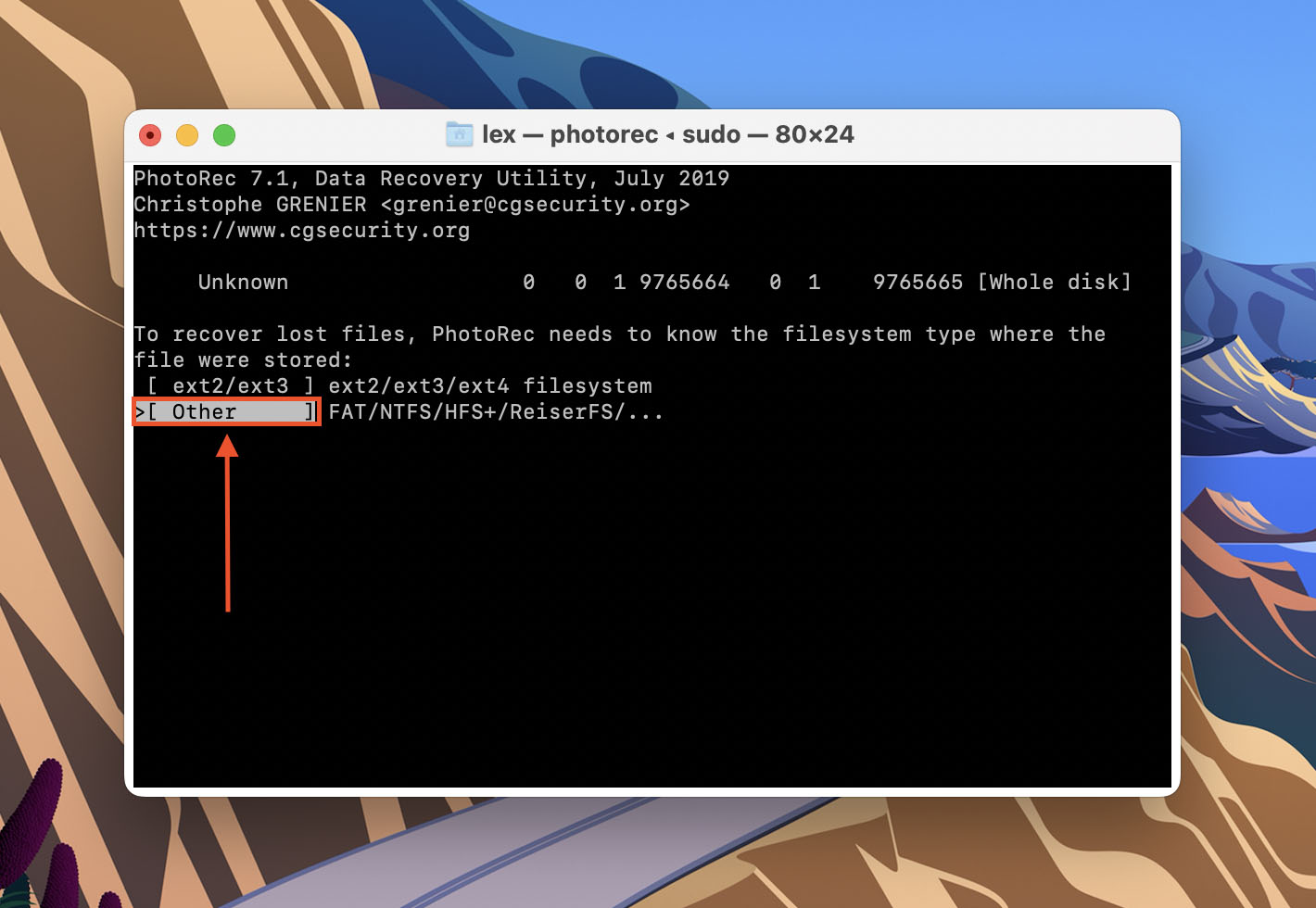
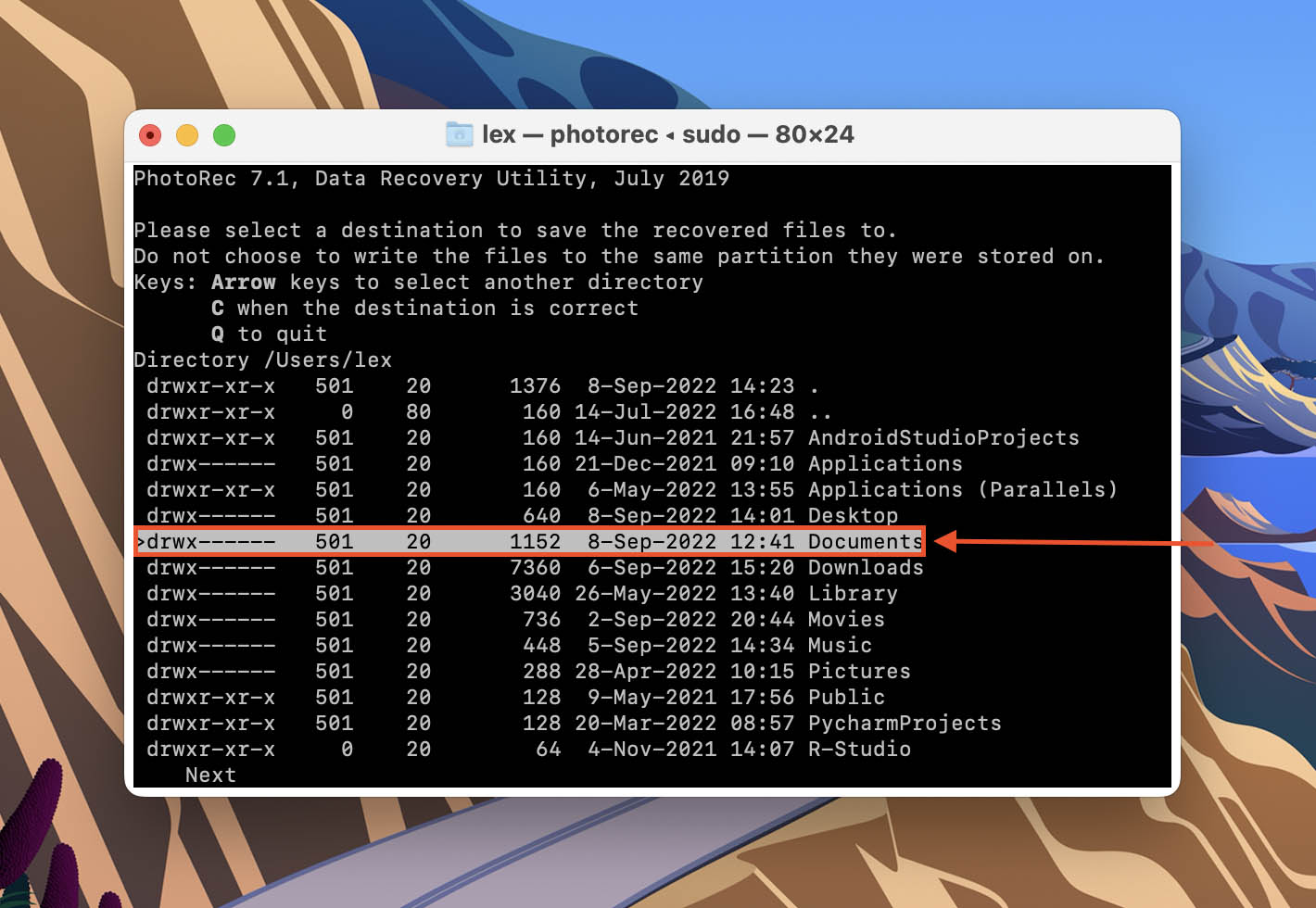
- Up your up and down arrow keys to browse folders. Use your left and right arrow keys to go in and out of the highlighted folder. Then, hit C to begin the recovery process.
Recover Files Deleted with RM Command on a Mac
RM is a powerful delete command that is super useful for users who want to delete a lot of files efficiently. Fortunately, RM does not overwrite files – however, it completely bypasses the Trash folder. So the only way to recover files deleted with RM command on a Mac is to use data recovery software.
We showed you how to use Terminal-based app PhotoRec in the last section. This time, we’ll be using a tool called Disk Drill. Unlike TestDisk/PhotoRec, Disk Drill has a well-designed interface that makes recovery simple for users at any level.
Note: Disk Drill Basic for Mac does not offer free data recovery. However, you can preview as many files as you want (including videos). There are free data recovery software aside form TestDisk/PhotoRec, but they all have their own limitations. Try at your own risk.
- Download and install Disk Drill.
- Launch Disk Drill (Finder > Applications).
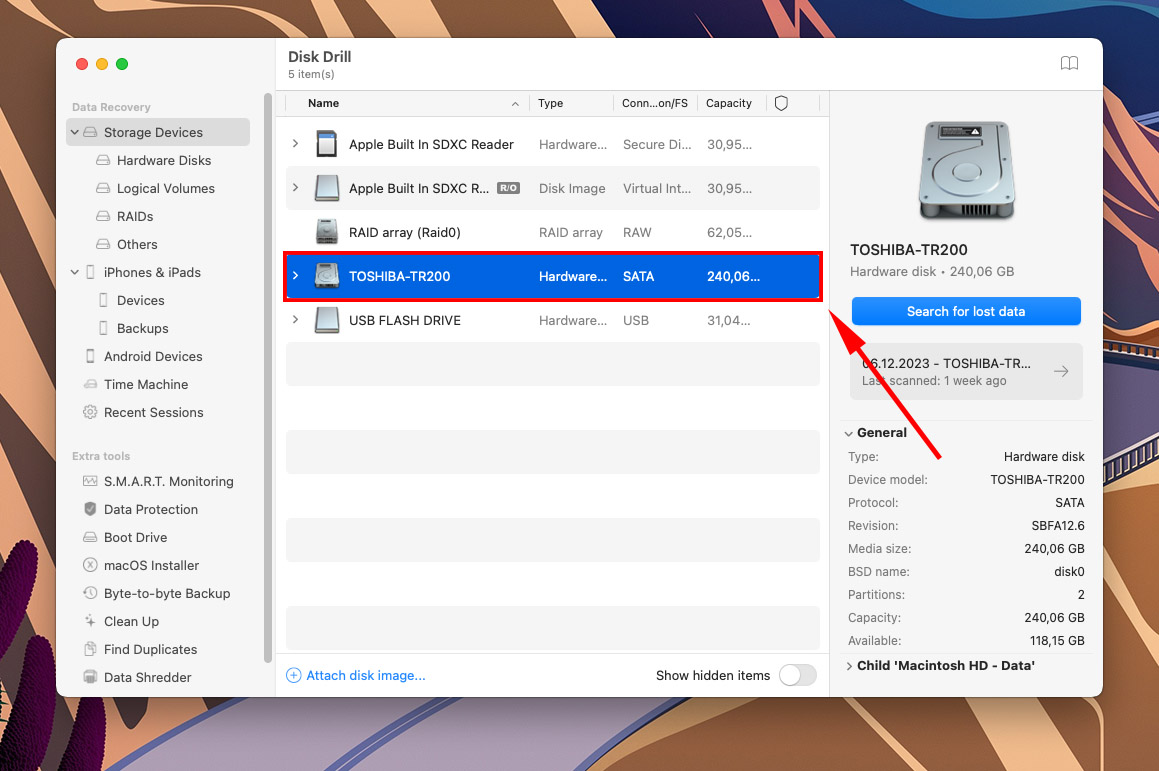
- Select the drive you want to restore (your system drive is usually labeled as “Apple SSD” or similar), then click Search for lost data.
- Wait for the scan to finish, then click Review found items.
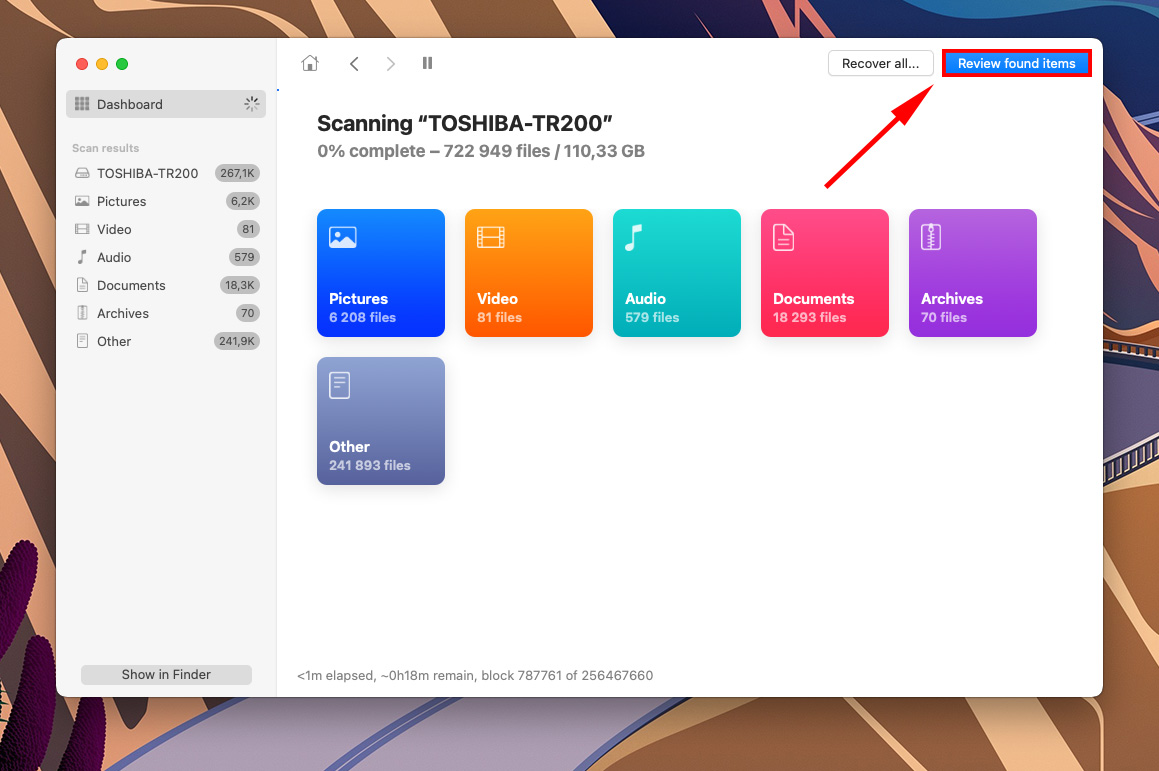
- Use the search bar in the top-right corner or select a file type from the left sidebar to narrow down the results.
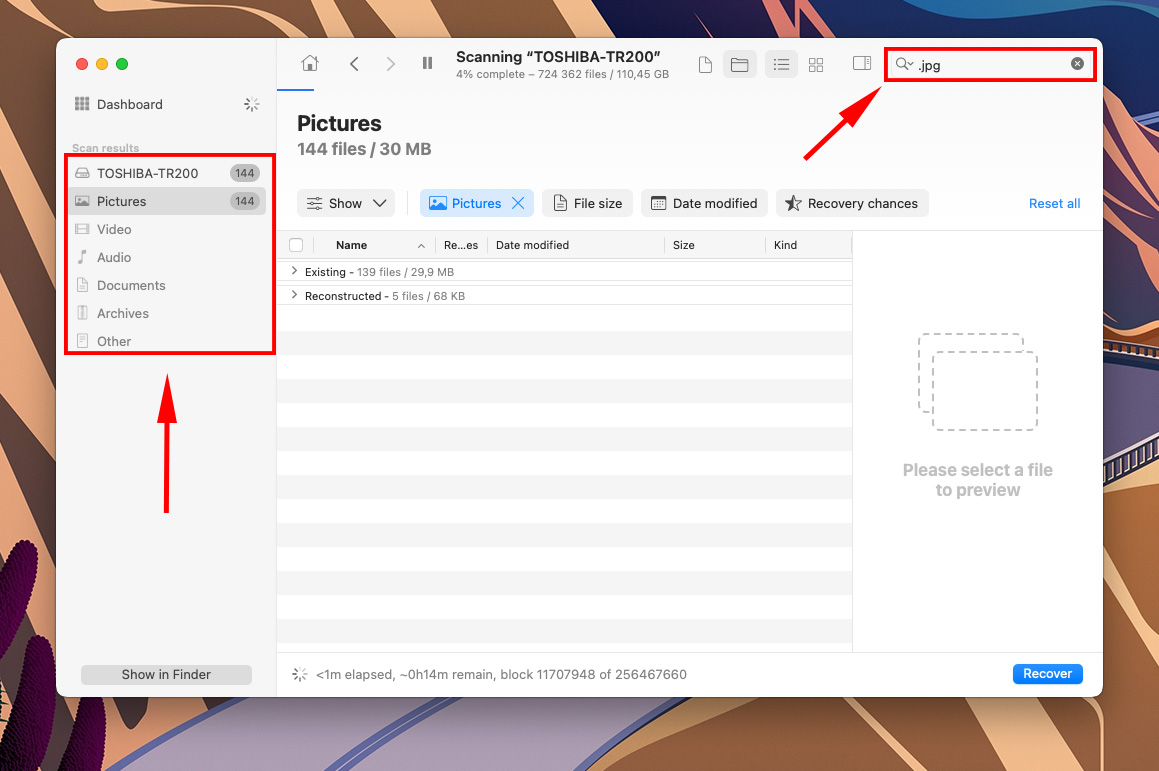
- To preview your files, hover your mouse pointer to the right of any file and click the eye button that appears.
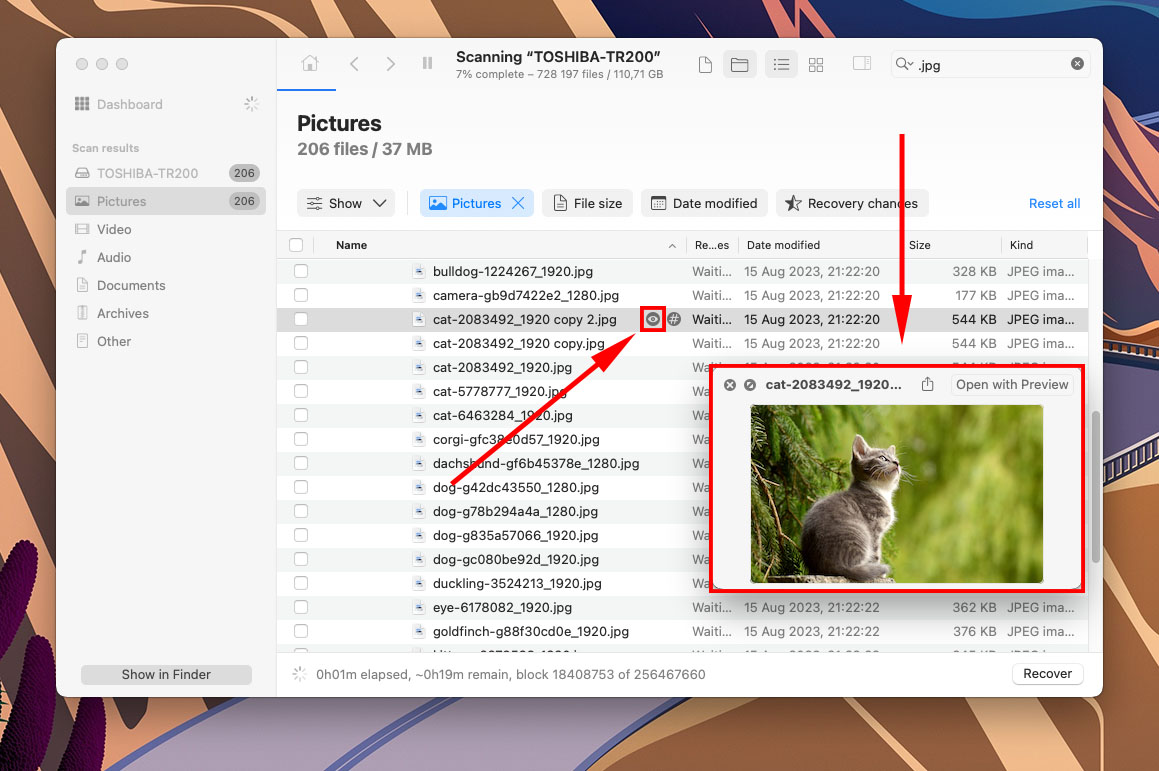
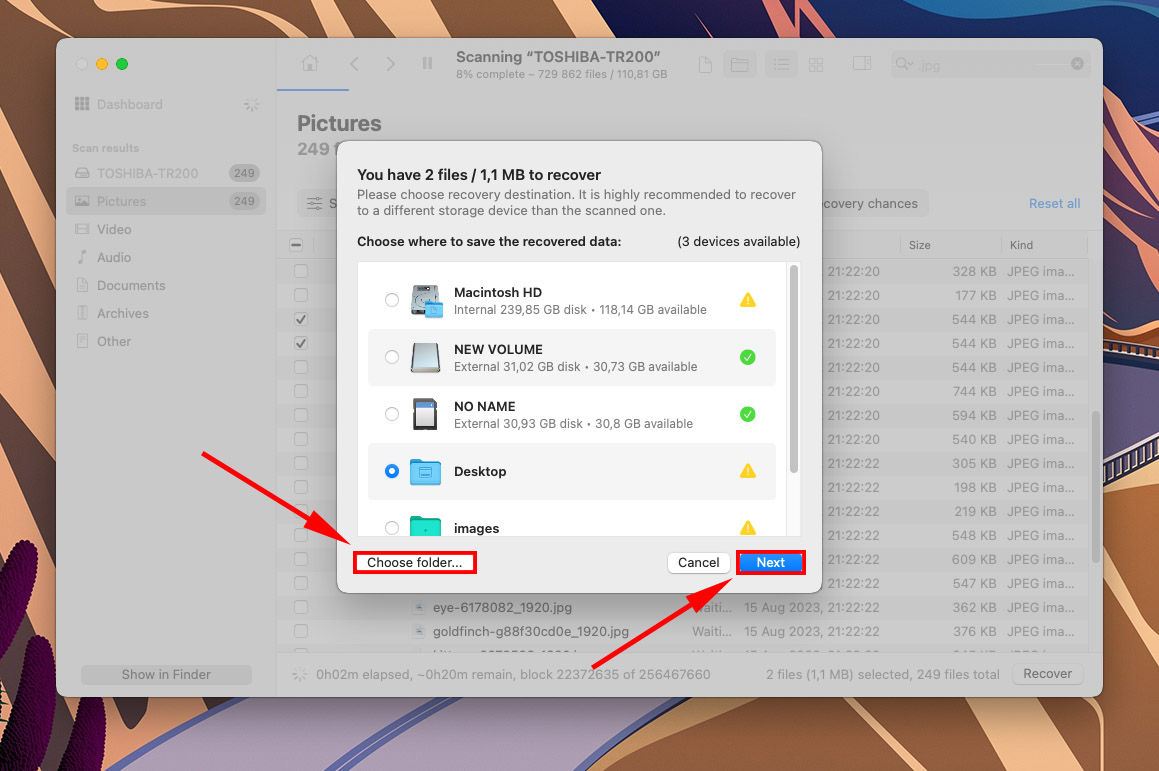
- Select the files you want to restore using the boxes in the left-most column. Then, click Recover.
- Use the Choose folder… button and select a location on a drive or partition that is different than the one we just scanned. Then, click Next.
Conclusion
Mac Terminal is powerful and efficient, and it’s a great way to restore your data all from a single window. But you know what’s even better? Backing up your files! We briefly covered Time Machine in one of the sections above – it’s super powerful and easy-to-use, so we highly recommend enabling it on your Mac.
FAQ
Yes! To recover permanently deleted files using Mac terminal, use the tmutil command to restore a Time Machine backup. Alternatively, use Terminal-based data recovery software like TestDisk/PhotoRec.
Yes! To recover emptied trash through the Mac Terminal, type the following commands and hit enter after each one:
-
cd. Trash
-
ls -al ~/.Trash
-
mv yourfile ../
Make sure to enable Full Disk Access for the Terminal app via System Preferences > Security & Privacy > Privacy tab.
You can’t directly undo rm -rf since it bypasses the Trash folder as it deletes files. However, you can undo the effects of data loss and restore rm files on your Mac by using data recovery software like TestDisk/PhotoRec or Disk Drill.
Absolutely! Your trusty Mac Terminal isn’t just for internal drives. With the right commands, you can rescue files from external drives too. Just connect the drive, open Terminal, and use similar recovery commands as you would for your Mac’s internal drive.
Indeed, there is! Mac Terminal can be your precision tool for this task. By using specific commands in Terminal-based recovery apps like TestDisk/PhotoRec, you can target specific file types.
