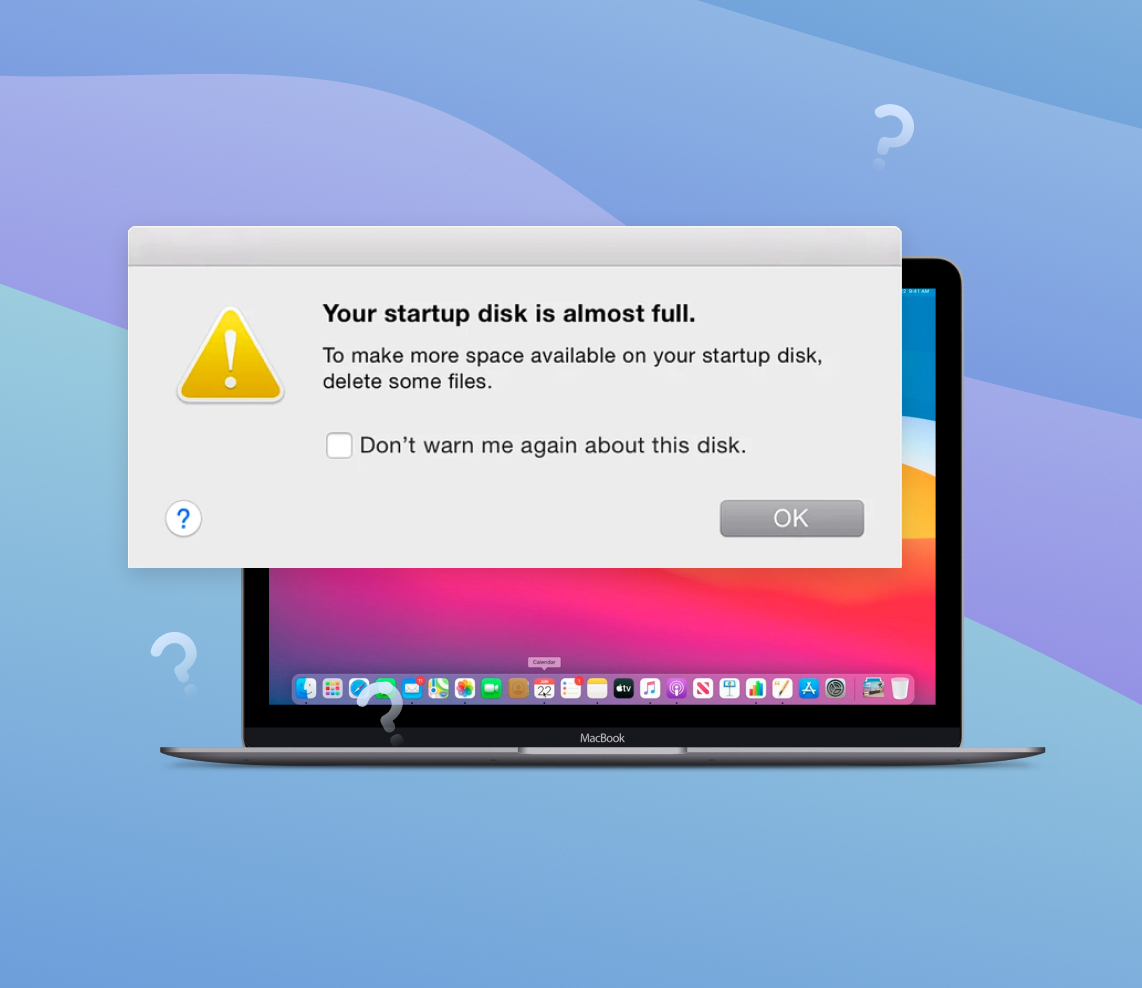
The concept of the startup disk on Mac computers plays a crucial role in the boot process. It houses the operating system, system files, applications, and user data, making it a vital component of the Mac’s functionality. While the default startup disk is usually the internal hard drive, multiple startup disks can be utilized through additional drives or partitions. Regular disk cleanup and maintenance are essential to address issues like low disk space and sluggish performance. This article delves into the significance of understanding and managing the startup disk on Mac systems.
Understanding the Startup Disk on Mac
When it comes to using a Mac computer, understanding the concept of the startup disk is essential. The startup disk plays a crucial role in the boot process and determines where the operating system and other files are stored. In this article, we will delve into the definition of the startup disk, explore its significance in the boot process, and explain how files and applications are stored on this disk.
What is a Startup Disk?
A startup disk on a Mac refers to the disk or partition that contains the operating system and other essential files required for the computer to boot up and run. It is the primary storage location for your Mac’s operating system, system files, applications, and user data.
By default, the startup disk is typically the internal hard drive of your Mac, known as the Macintosh HD. However, it is possible to have multiple startup disks if you have multiple drives or partitions on your Mac. The startup disk is designated as the boot volume, meaning it is the disk from which the Mac boots up and launches the operating system.
The Role of the Startup Disk in the Boot Process
During the boot process, the Mac searches for the startup disk to locate the necessary system files and the operating system. It reads the boot loader, a small program stored on the startup disk, which then loads the macOS or Mac OS X kernel, initiating the operating system’s launch.
Once the operating system is loaded, it takes control of the Mac, allowing you to access your files, applications, and perform various tasks. The startup disk continues to play a vital role even after the boot process, as it remains the primary storage location for all your data and software.
How Files and Applications are Stored on the Startup Disk
The startup disk is divided into multiple partitions or volumes, with each volume having its own file system. These partitions can be formatted in various ways, such as APFS (Apple File System) or HFS+ (Hierarchical File System Plus), depending on the version of macOS you are using.
When you install applications or save files on your Mac, they are typically stored on the startup disk by default. The operating system ensures that the files and applications are organized within the appropriate directories or folders on the startup disk. The directory structure allows easy access to your files and helps the system locate the required data efficiently.
Over time, as you use your Mac, the startup disk may accumulate temporary files, cache data, and other unnecessary items, leading to a decrease in available disk space. This can result in a disk full error or slow performance. To address these issues, it is important to perform regular disk cleanup and maintenance.
Signs of a Full Startup Disk
A full startup disk on a Mac can lead to various issues and affect the overall performance of your computer. It’s important to be aware of the signs that indicate a full startup disk so that you can take appropriate action to resolve the problem. Here are some common symptoms to watch out for and the importance of addressing a full startup disk promptly:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| ⚠️ Low Disk Space Warnings | One of the primary indicators of a full startup disk is the appearance of low disk space warnings on your Mac. You may receive pop-up notifications or see alerts stating that your disk space is running out. These warnings serve as an early warning system, alerting you to the need for disk cleanup to free up space on your startup disk. |
| ? Sluggish Performance | A full startup disk can significantly impact the performance of your Mac. As the disk space becomes limited, your computer may start to slow down, take longer to open applications, and experience delays when accessing files. This can be frustrating and hinder your productivity. If you notice a significant decrease in performance, it’s likely that your startup disk is nearing its capacity. |
| ? Inability to Save Files | When your startup disk is full, you may encounter difficulties when attempting to save new files or create backups. Your Mac may display error messages indicating that there is not enough disk space to complete the operation. This can be particularly problematic if you’re working on important projects or need to back up essential data. It’s crucial to address the full startup disk issue to ensure you can continue saving and accessing your files seamlessly. |
| ? Unresponsive Applications | As the startup disk approaches its maximum capacity, you may experience unresponsiveness or crashes in certain applications. This occurs because the applications require temporary disk space to function properly. When there is insufficient space, the applications may freeze, become unresponsive, or unexpectedly quit. Resolving the full startup disk will help restore the stability and responsiveness of your applications. |
| ⬆️ Difficulty Installing Updates | Updating your macOS and applications is essential for security, bug fixes, and new features. However, a full startup disk can hinder the installation of these updates. When your disk is full, there may not be enough space to download and install updates, leading to errors or incomplete installations. It’s crucial to free up disk space to ensure a smooth update process and keep your system up to date with the latest improvements and security patches. |
The Importance of Identifying and Resolving a Full Startup Disk
It’s essential to promptly identify and resolve a full startup disk on your Mac. Ignoring the issue can lead to further complications and negatively impact your computer’s performance. Here’s why it’s important:
- Prevent Data Loss: A full startup disk increases the risk of data loss, especially if you don’t have sufficient space for automatic backups or when your applications cannot save files properly. Resolving the full startup disk issue helps safeguard your important data.
- Improve Performance: Freeing up disk space by cleaning up your startup disk can significantly improve the performance of your Mac. It allows the operating system and applications to function optimally and ensures smooth multitasking and responsiveness.
- Enable Updates and Upgrades: Keeping your Mac and applications up to date is crucial for security, compatibility, and access to new features. By resolving a full startup disk, you can ensure sufficient space for installing updates and upgrades without interruptions.
If you suspect that your startup disk is full, it’s recommended to perform a disk cleanup and remove unnecessary files, duplicates, or large items that are consuming valuable disk space. Regular maintenance and disk cleanup can help prevent the recurrence of a full startup disk and maintain your Mac’s optimal performance.
For more detailed instructions on how to clear the startup disk on a Mac, you can refer to the official Apple support documentation: https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT206996.
Cleaning Up Startup Disk on Mac
In order to optimize the performance of your Mac and free up valuable disk space, it’s essential to clean up the startup disk regularly. In this section, we will explore various methods to clean up the startup disk on a Mac.
Method 1: Remove Unnecessary Files
The first step is to identify and remove unnecessary files from your startup disk. Here are a few areas to focus on:
- Downloads Folder: Check your Downloads folder for any files you no longer need and delete them.
- Documents and Files: Review your documents, media files, and other personal data. Delete any files that are no longer necessary.
- Large Files: Use the built-in “All My Files” option in the Finder to sort files by size and identify large files that you can delete or move to an external storage device.
Method 2: Uninstall Unneeded Applications
Uninstalling applications that you no longer use can help free up significant disk space. To uninstall applications on a Mac, follow these steps:
- Open the Finder and go to the “Applications” folder.
- Locate the application you want to uninstall.
- Right-click on the application and select “Move to Bin.”
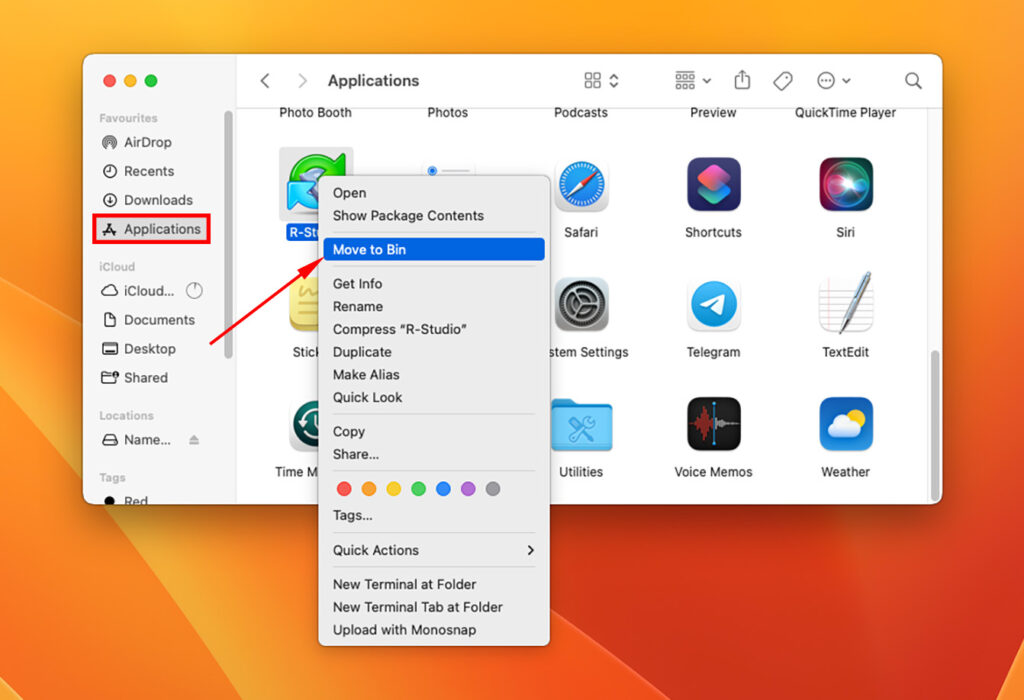
- Empty the Trash to permanently delete the application.
Method 3: Clear Cache and Temporary Files
Cache and temporary files generated by applications can take up valuable space on your startup disk. Here’s how you can clear them:
- Using Built-in Tools: Some applications, such as web browsers, have built-in options to clear their cache and temporary files. Check the preferences or settings of the specific applications you use.
- Third-Party Cleaning Software: Third-party cleaning software like CCleaner or CleanMyMac can help you remove cache and temporary files from various applications. These tools often provide an easy-to-use interface to clean up your system.
- Application-Specific Cache: Certain applications, especially multimedia or video editing software, may store cache files. You can usually find an option within the application’s preferences or settings to clear the cache. Refer to the documentation or support resources for the specific application you are using.
- Clear System Caches: To clear system caches on your Mac, you can use the built-in “Maintenance” feature of third-party cleaning software like CleanMyMac or Onyx. These tools can help you safely remove temporary files and system caches that are no longer needed.
- Manually Delete Cache Files: If you prefer to manually delete cache files, you can navigate to the following location on your Mac and remove the cache files associated with specific applications:
- ~/Library/Caches
- /Library/Caches
- /System/Library/Caches
However, be cautious when manually deleting cache files, as removing the wrong files can potentially cause issues with the associated applications. It’s recommended to use reliable third-party cleaning software or follow specific instructions provided by the application developers.
Method 4: Offload Files to External Storage
If you have large files or data that you don’t frequently access, you can consider offloading them to external storage devices like external hard drives or cloud storage. This way, you can free up space on your startup disk without permanently deleting the files. Cloud storage services like iCloud, Dropbox, or Google Drive can be useful for storing files offsite while still having convenient access to them.
Method 5: Empty the Trash
Remember to regularly empty the Trash on your Mac to permanently delete the files and recover disk space. You can either right-click on the Trash icon in the Dock and select “Empty Trash” or use the “Empty Trash” option from the Finder menu.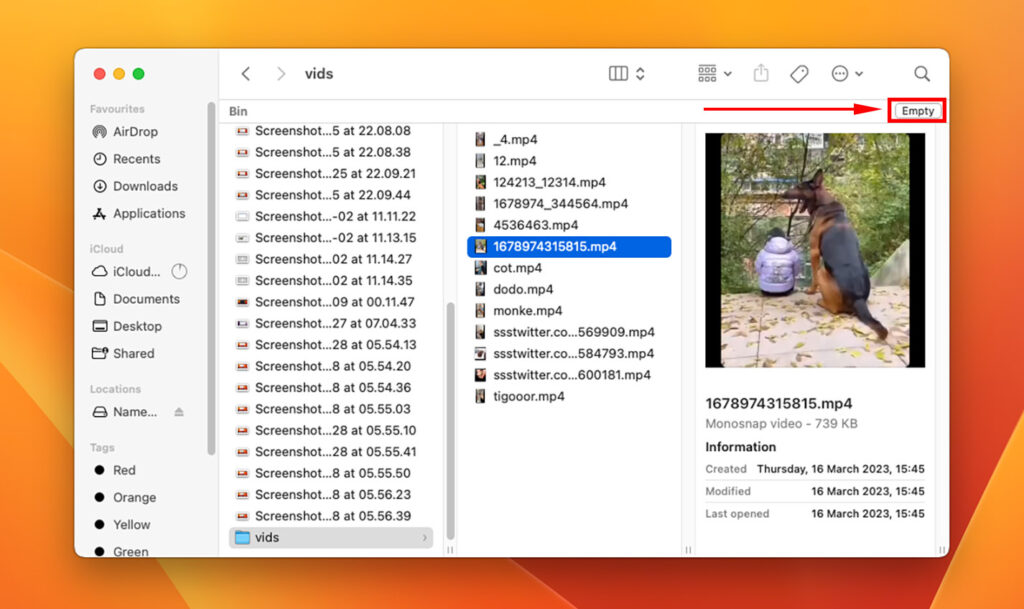
Cleaning up the startup disk on your Mac is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and freeing up disk space. By removing unnecessary files, uninstalling unneeded applications, utilizing the built-in Storage Management tool, clearing cache and temporary files, offloading files to external storage, and emptying the Trash, you can keep your Mac running smoothly and efficiently.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the startup disk is a fundamental aspect of Mac computers, housing the necessary components for booting and running the operating system. By properly managing the startup disk and ensuring sufficient disk space, users can optimize their Mac’s performance and avoid potential issues. Regular disk cleanup, removal of unnecessary files, and utilizing additional storage options when needed are crucial steps in maintaining a healthy startup disk. Understanding the role of the startup disk empowers users to effectively manage their Mac systems and enjoy a seamless computing experience.
There can be a few reasons why your Mac may display a “not enough disk space” message even when you believe there is sufficient space:
- Temporary files and caches taking up space.
- Large files or applications that are consuming a significant portion of your storage.
- Fragmented files that may not be utilizing disk space efficiently.
- Issues with the Spotlight indexing system.
Yes, Mac provides built-in disk cleanup features to help you manage and optimize your storage. You can utilize the storage optimization settings, which we discussed earlier, to remove unnecessary files and reclaim disk space. Additionally, you can manually delete files, empty the Trash, and use third-party cleaning software for a more thorough disk cleanup.
The performance of your Mac depends on various factors beyond storage space. Here are a few reasons why your Mac may be slow despite having ample storage:
- Insufficient RAM (Random Access Memory).
- Background processes consuming system resources.
- Outdated software or operating system.
- Fragmented files and disk errors.
Performing regular maintenance tasks like cleaning up your startup disk, optimizing storage settings, updating software, and restarting your Mac can help improve its performance.
Restarting your Mac startup disk refers to restarting your computer. When you restart your Mac, the system shuts down and boots up again, which can help refresh system processes and clear temporary data. It does not format or erase your startup disk. However, it’s always a good practice to back up your important files before restarting your Mac to ensure the safety of your data.