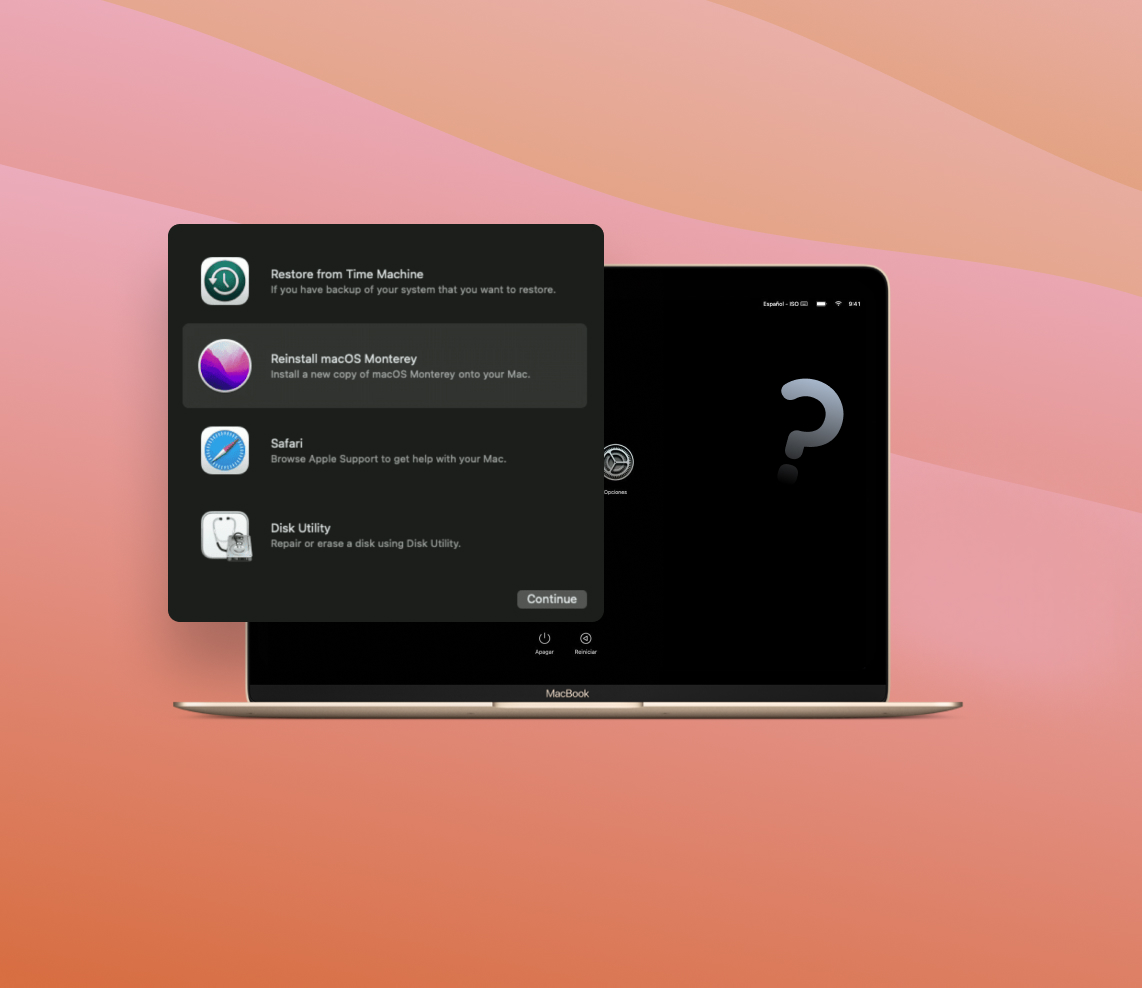
When it comes to troubleshooting and resolving issues on your Mac, to boot Mac in Recovery Mode is your go-to resource. Packed with essential tools and utilities, this built-in feature provides the means to reinstall macOS, repair disks, restore from backups, and perform system maintenance tasks. Whether you’re facing operating system glitches, hard drive troubles, malware infections, firmware password issues, or file recovery challenges, Recovery Mode has got you covered. With its comprehensive features and easy accessibility, Mac Recovery Mode ensures that your Mac stays on track, delivering optimal performance.

Understanding Mac Recovery Mode
Mac Recovery Mode is a built-in feature in macOS that provides essential tools and utilities to troubleshoot and repair various issues that may arise on your Mac. Whether you need to reinstall macOS, repair a disk, restore from a Time Machine backup, or perform other system maintenance tasks, Recovery Mode is a powerful resource that can help you get your Mac back on track.
Features of Recovery Mode
Recovery Mode offers several key features that enable users to diagnose and resolve software-related problems:
- Reinstall macOS: This option allows you to download and reinstall the latest version of macOS without affecting your personal files or settings. It can be handy when your Mac is experiencing persistent issues or if you want a fresh start.
- Restore from Time Machine: If you have a Time Machine backup, you can use Recovery Mode to restore your Mac to a previous state. This feature is particularly useful when you want to revert to a stable configuration or recover lost data.
- Disk Utility: Recovery Mode includes Disk Utility, a tool for managing and repairing your Mac’s storage. You can use it to format disks, repair disk errors, create disk images, and perform other disk-related tasks.
- Terminal: Recovery Mode provides access to the Terminal, a command-line interface that allows advanced users to execute commands and perform system-level operations for troubleshooting purposes.
Scenarios Where Recovery Mode Can Be Helpful
There are several situations where accessing Recovery Mode can be beneficial:
| ?️ Operating System Issues | If your Mac is encountering frequent crashes, startup problems, or issues with system files, Recovery Mode can help you diagnose and fix these problems. |
| ? Hard Drive Troubles | When you suspect disk errors, file system corruption, or other storage-related issues, using Recovery Mode’s Disk Utility can assist in repairing or reformatting the drive. |
| ? Malware Removal | In the unfortunate event of a malware infection, Recovery Mode can be utilized to scan your Mac for malicious software and remove it effectively. |
| ? Firmware Password | If you have set a firmware password and forgotten it, Recovery Mode can help you reset it, granting access to your Mac again. |
| ? File Recovery | If you accidentally deleted important files or folders, Recovery Mode allows you to restore them from a Time Machine backup or attempt data recovery using specialized tools. |
It’s important to note that accessing Recovery Mode may slightly differ depending on your Mac model. However, it is available on both Intel-based Macs and the latest M1/M2-based Macs.
Now that you understand the concept and significance of Mac Recovery Mode, you can confidently tackle various issues that may arise on your Mac, ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance.
Methods to Boot Mac in Recovery Mode
When encountering issues with your Mac, entering recovery mode can be a helpful troubleshooting step. Recovery mode provides access to various tools and utilities that can assist in resolving problems or reinstalling macOS. Here are three methods to boot your Mac into recovery mode:
Method 1: Using Startup Manager
If you want to access recovery mode through the Startup Manager, follow these steps:
- Start or restart your Mac.
- Press and hold the Option (⌥) key immediately after the startup chime.

- You will see the Startup Manager window, which displays available startup disks.
- Use the arrow keys to select the Recovery disk.
- Press Return or click on the Recovery disk to start your Mac in recovery mode.
Method 2: Using Keyboard Shortcut
There is a specific keyboard shortcut that allows you to directly access recovery mode. Follow these instructions:
- Start or restart your Mac.
- Immediately press and hold the Command (⌘) and R keys together.

- Continue holding the keys until the Apple logo or a spinning globe appears.
- Your Mac will boot into recovery mode.
Recovery Mode on M1-based Macs
For M1-based Macs, the process of entering recovery mode differs slightly. Here’s how to access recovery mode on an M1-based Mac:
- Start or restart your Mac.
- Press and hold the Power button until you see the startup options.
- Select the Options icon to access the Startup Manager.
- Use the arrow keys to select the Recovery disk.
- Press Return or click on the Recovery disk to start your Mac in recovery mode.
For more detailed information about Mac recovery mode, you can refer to the official Apple support document on macOS Recovery. This guide provides additional insights and instructions to help you navigate through recovery mode effectively.
Performing Tasks in Recovery Mode
Recovery Mode is a powerful feature on Mac computers that allows users to troubleshoot and perform various tasks to restore their system or resolve issues. Whether you need to reinstall macOS, restore from a backup, orperform other maintenance tasks, Recovery Mode provides a range of options to help you get your Mac back on track.
Once you’re in Recovery Mode, you’ll be presented with a range of options to choose from.
Reinstalling macOS
If you’re experiencing major issues with your Mac or want a fresh start, you can reinstall macOS using Recovery Mode. This process allows you to install the latest version of macOS without affecting your personal files. Here’s how:
- In Recovery Mode, select “Reinstall macOS” from the options.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to proceed with the reinstallation process.
For detailed instructions and additional information, you can refer to the official Apple support article on reinstalling macOS.
Restoring from a Backup
If you have a recent backup of your Mac’s data, you can use Recovery Mode to restore your system to a previous state. This is especially useful if you encounter data loss or want to revert to a stable configuration. Here’s what you need to do:
- In Recovery Mode, select “Restore from Time Machine Backup” or “Restore from Mac Backup” depending on your backup source.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to select the appropriate backup and initiate the restoration process.
For detailed instructions and additional information, you can visit the official Apple support page on restoring from a Time Machine backup.
Using Disk Utility and Troubleshooting Tools
Recovery Mode provides access to Disk Utility and other troubleshooting tools that can help diagnose and repair issues with your Mac’s storage and system files. Here’s how you can utilize these tools:
- In Recovery Mode, select “Disk Utility” to launch the utility.
- Use Disk Utility to repair disk errors, erase and partition drives, or perform other disk-related tasks.
- If Disk Utility doesn’t resolve the problem, you can explore additional troubleshooting tools available in Recovery Mode, such as “Terminal” for advanced command-line operations.
For detailed instructions and additional information, you can refer to the official Apple support article on using Disk Utility and additional troubleshooting tools.
Variations and Limitations for M1-based Macs
M1-based Macs, powered by Apple’s custom silicon, have introduced changes to the recovery process compared to Intel-based Macs. While the overall functionality remains similar, there are a few key differences to note:
- On M1-based Macs, no keys except the power button need to be held during startup to enter Recovery Mode.
- Recovery Mode on M1-based Macs supports macOS Recovery over the Internet, allowing you to reinstall macOS even if your Mac’s internal recovery system is unavailable.
For more information on the recovery process for M1-based Macs, you can visit the official Apple support page on recovery options for Apple Silicon Macs.
Performing tasks in Recovery Mode is a valuable skill for Mac users, empowering them to troubleshoot and resolve various issues that may arise. By understanding the available options and their limitations, you can effectively restore your Mac’s functionality and keep it running smoothly.
Pro-Tip: Check the Internet Connection
In recovery mode, a stable internet connection is crucial for various troubleshooting tasks. Whether you need to reinstall macOS or restore from a backup, ensuring a reliable internet connection is essential. Here are the steps to check and establish a stable internet connection:
- Connect your Mac to a Wi-Fi network or use an Ethernet cable for a wired connection.
- Ensure that your internet service is working correctly by testing it on other devices.
- Restart your modem and router.
- Reset the network settings on your Mac by going to “System Preferences,” selecting “Network,” and clicking on the “Advanced” button. Then, choose “Renew DHCP Lease” and “Apply.”
For M1-based Macs, it’s important to note that some early models might encounter issues with Wi-Fi connectivity in recovery mode. If you experience difficulties, consider connecting via Ethernet for a more reliable connection.
Conclusion
Mac Recovery Mode is a vital tool for Mac users, offering a range of features and options to troubleshoot and resolve issues. Whether you need to reinstall macOS, restore from a backup, or perform disk-related tasks, Recovery Mode provides the necessary tools to keep your Mac running smoothly. By understanding the methods to access Recovery Mode and the tasks you can perform within it, you can confidently address software-related challenges and ensure optimal performance. Remember to consult official Apple support resources for detailed instructions and further assistance. With Mac Recovery Mode, you have a reliable tool at your disposal to overcome various problems and maintain the functionality of your Mac.
FAQ
To start your Mac directly in Disk Utility, you can follow these steps:
- Start or restart your Mac.
- Immediately press and hold the Command (⌘) and R keys together.
- Keep holding the keys until the Apple logo or a spinning globe appears.
- Once you’re in recovery mode, select “Disk Utility” from the available options.
- You can now use Disk Utility to format, repair, or manage your drives.
If you’re using a Windows keyboard with your Mac and want to access Disk Utility, you can try the following steps:
- Start or restart your Mac and hold down the Windows and R keys.
- When the startup disk selection screen appears, use the arrow keys on your Windows keyboard to navigate and highlight the disk with the macOS or recovery system you want to use.
- Press the Return (⏎) key to boot into the selected disk.
- Once your Mac boots up, go to the Utilities menu and select Disk Utility to access and manage your drives.
The startup disk refers to the disk or partition from which your Mac boots up. In recovery mode, you can select a startup disk to boot from, which allows you to perform various disk-related tasks, such as repairing or formatting drives. It’s important to choose the correct startup disk to ensure you’re working with the intended drive.
There could be several reasons why you are unable to access recovery mode on your Mac. It could be due to a faulty keyboard, a problem with your macOS installation, or an issue with the recovery partition. Make sure your keyboard is functioning properly, try resetting the NVRAM or PRAM, and ensure that your macOS is up to date. If the problem persists, it’s recommended to contact Apple Support for further assistance.